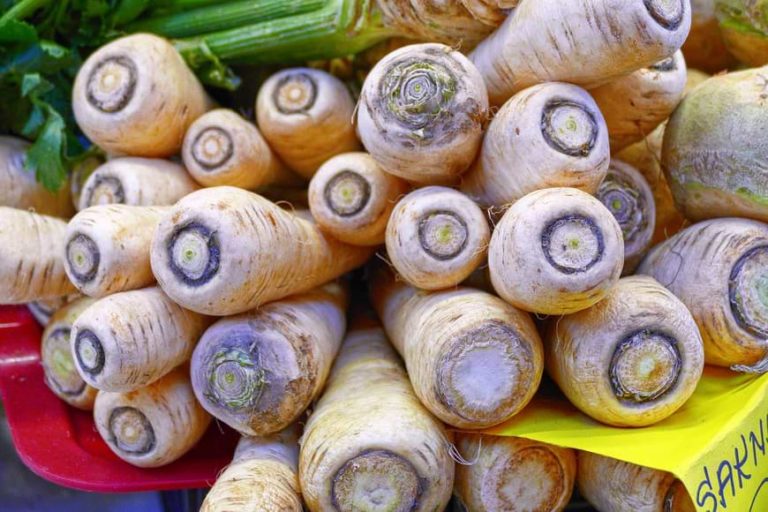
One of the less popular vegetables on the market and for kids, the parsnip is actually one of the most underrated vegetables in terms of flavor and health benefits. Contrary to popular belief, parsnips and turnips are two separate vegetables and parsnips are not the result of a parsley and turnip cross-breed. With very little people knowing a lot about parsnips, though, its flavor in vegan, vegetarian, or meat-based dishes is often overlooked. And its nutritional value also cannot be ignored.
What Is a Parsnip?
A parsnip is a type of root vegetable. At first glance, it may look like a pale carrot with a parsley-filled top, and for a good reason: parsnips, carrots, and parsley belong to the Apiaceae family. In scientific terms, a parsnip is known as the Pastinaca sativa.

It is a biennial plant, which means it takes two years to grow and die. To survive the winter, it enters a period of dormancy while it waits out the cold. Parsnips are a root crop, meaning it is buried underground. When it “hibernates” during the winter frosts, its flavor changes into something sweeter.
Early Uses of Parsnips
Throughout history, the parsnip has often been confused with the similar-looking carrot. While parsnips are available in almost everywhere in the world, they were originally from Eurasia. Historical evidence suggests that the Romans had grown it during their time and was used as a natural sweetener before cane sugar and beet sugar were discovered. It was believed that parsnips were an aphrodisiac, but it wasn’t a staple in Roman (and later Italian) cuisine. Instead, it was fed to pigs that were used to make Parma ham.
In China, Chinese parsnips were an ingredient for herbal medicines. Parsnips were brought to North America during the mid-19th century. This traces back to the French colonists that settled in Canada as well as the British in the Thirteen Colonies. For a while it served as the main source of starch until it was replaced by potatoes, which were much easier to cultivate.
Uses for Parsnips
Parsnips harvested and used for food consumption have a sweeter taste. Like carrots, it can be eaten raw, but cooking it through many different ways releases its sweet flavors. When used in stews, soups, and other liquid-based food, the parsnips provide a rich flavor and its starch can be used to thicken the dish. Parsnips are very similar to carrots and potatoes and can be a substitute for these two in certain dishes. Here’s an example of creamy mashed parsnips instead of using a traditional potato.
Outside of food, parsnips can be made into a wine. If it sounds disgusting, don’t knock it until you try it. People who have tried parsnip wine claims it has a sweet and dry wine that’s stronger than other fruit or vegetable-based wines. One glass of parsnip wine is potent enough to get men with low to average alcohol tolerance drunk.
What Is the Difference Between Parsnip and Turnip?
Contrary to popular belief, just because these two vegetables sound similar does not mean they are anything alike. While parsnips resemble carrots, turnips resemble onions. Ironically, though, turnips have the leaves that resemble those of carrots. However, turnips do not belong to the same family as parsnips and carrots.

The parsnip’s name, pastinaca, most likely comes from either the Latin word pastino, which means “to prepare the ground for planting the vine,” or pastus, which means food. A common misconception is that a parsnip is the result of cross-breeding a parsley and turnip plant, but this is not true. However, due to folk etymology, most people considered this to be true.
How Healthy Are Parsnips?
Like carrots, parsnips can either be eaten raw or cooked in various ways. Like many root crops, it is rich in vitamins and minerals and is a good vegetable choice for people with hypokalemia or potassium deficiency. It is also rich in antioxidants and fiber.
Aside from multiple vitamins and minerals, parsnips provides multiple potential benefits. It is rich in antioxidants like falcarinol and methyl-falcarindiol which may have anti-inflammatory and anti-fungal effects.
Too Much Parsnips?
While it is a healthy vegetable, like a lot of things, too much of it can be bad for your health. While parsnips are rich in potassium and can help those with deficiencies, too much of it in your blood can lead to hyperkalemia which shows symptoms like nausea, fatigue, and cramps. In some cases, too much can affect the way your heart muscles work and make you feel chest pains or unusual heartbeat rhythms.
Too much vitamins from parsnips can also lead to vitamin overdoses, which can also have a negative effect on your body. One of parsnip’s vitamins, for example, is vitamin C; too much of this can lead to diarrhea and stomach cramps.
Toxicity of Parsnips
Handling the stems, shoots, and leaves of parsnips can cause skin rashes especially if the part of the skin that touched these part of the parsnip are exposed to sunlight. While handling and cooking parsnips is generally safe and edible, its sap (like the rest of the vegetables in the Apiaceae family) is toxic and contains phototoxic chemicals that cause a condition known as phytophotodermatitis.
A person experiencing this can have rashes, red skin, burning, and blisters. A small number of people have experienced these symptoms while handling parsnips, and the discoloration can stay on your skin for around two years. Because of this, parsnip farmers only harvest parsnips during the winter or when it isn’t a sunny day to reduce the effects of the toxins. When done properly, the effects of parsnip sap is very mild.
While parsnips aren’t very popular and have a small amount of risk, it is a delicious root that provides a unique flavor when used in food products and dishes. If you have a potassium deficiency and want a vegetable that’s rich in minerals and flavor, try replacing the potatoes, carrots, or any similar root vegetable in your favorite dish with parsnip instead. The flavor might be different, but at least it will be an experience you definitely won’t forget.